Divine Info About How To Check For Normal Distribution
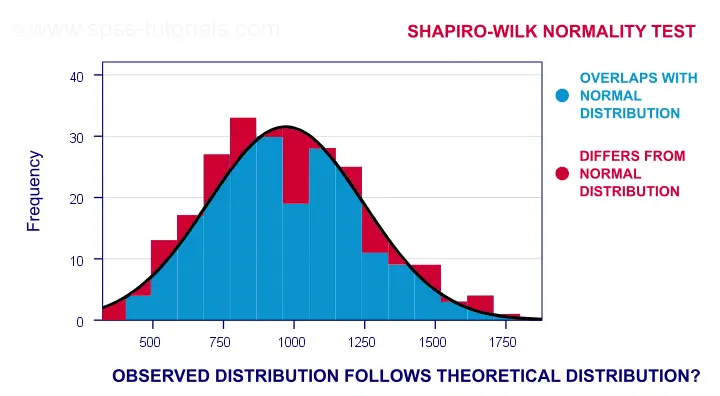
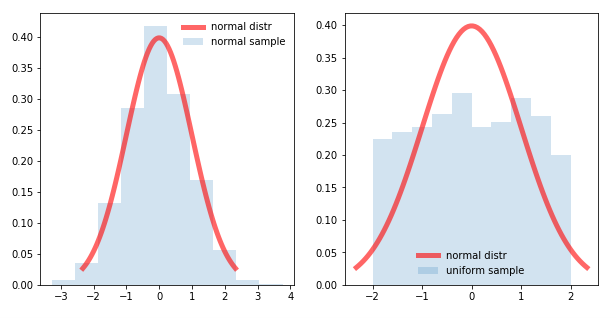
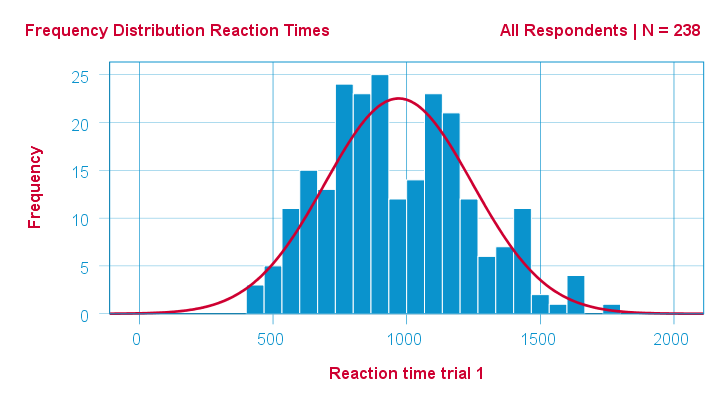
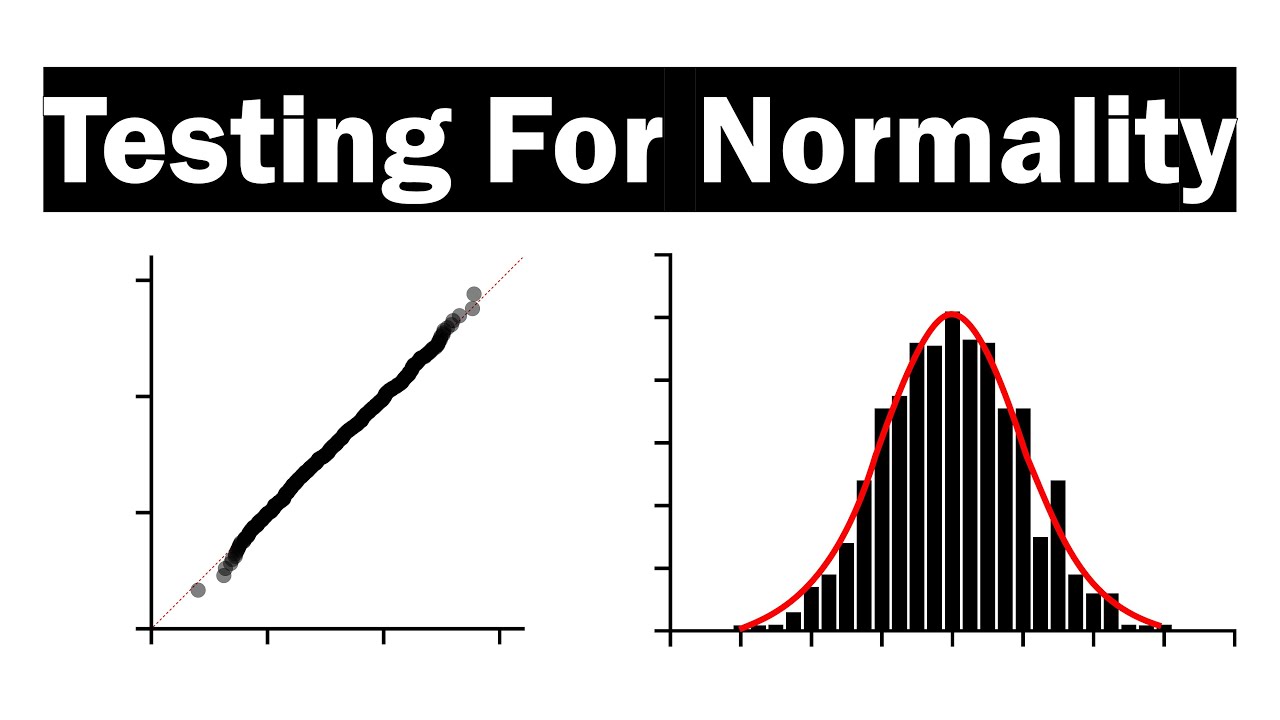
To test for normality using a histogram, you compare the histogram of the data set to the normal probability curve.
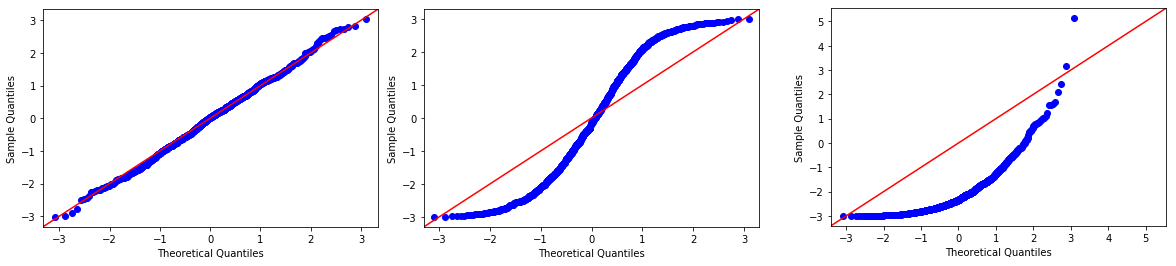
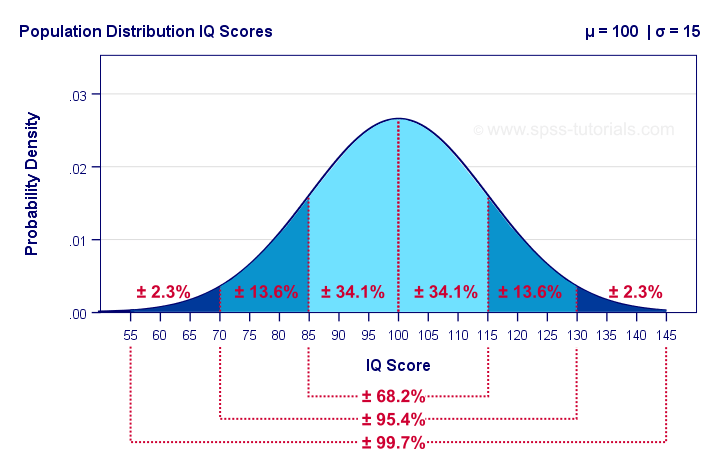
How to check for normal distribution. 95% is 2 standard deviations either side of the mean (a total of 4 standard deviations) so: There are four common ways to check this assumption in r: If the shape of the distribution resembles a bell curve, the data is likely normal.
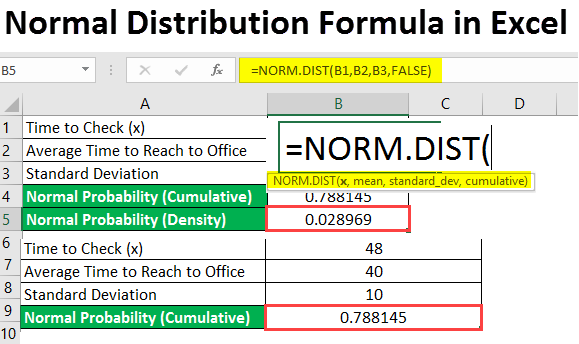
X is a value or test. Here’s what you need to assess whether your data distribution is normal. Μ (“mu”) is a population mean;
The area under the whole curve is equal to 1, or 100%. And this is the result: You can use the following methods to plot a normal distribution with the seaborn data visualization library in python:
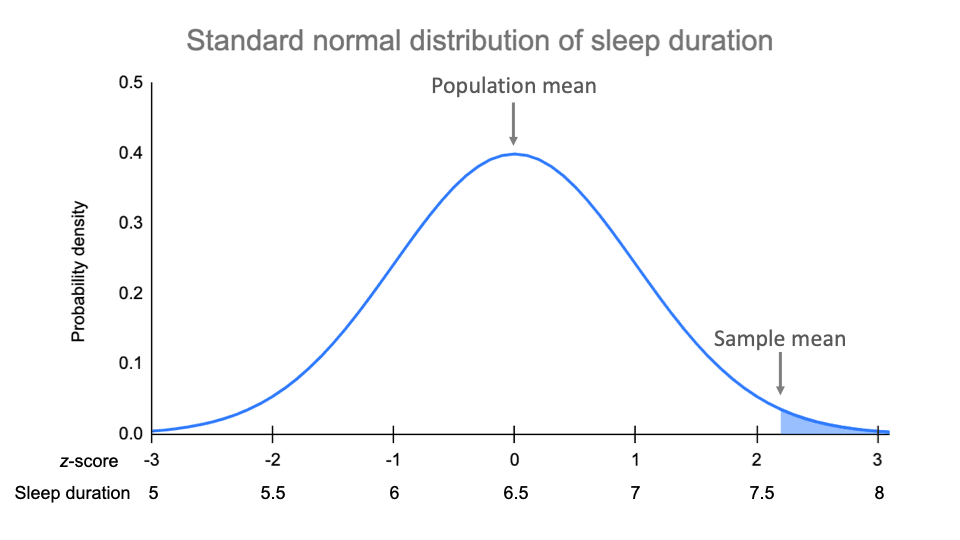
Mean = (1.1m + 1.7m) / 2 = 1.4m. If your variable has a normal distribution, we should see a bell curve. It is good to know the standard deviation, because we can say that any value is:
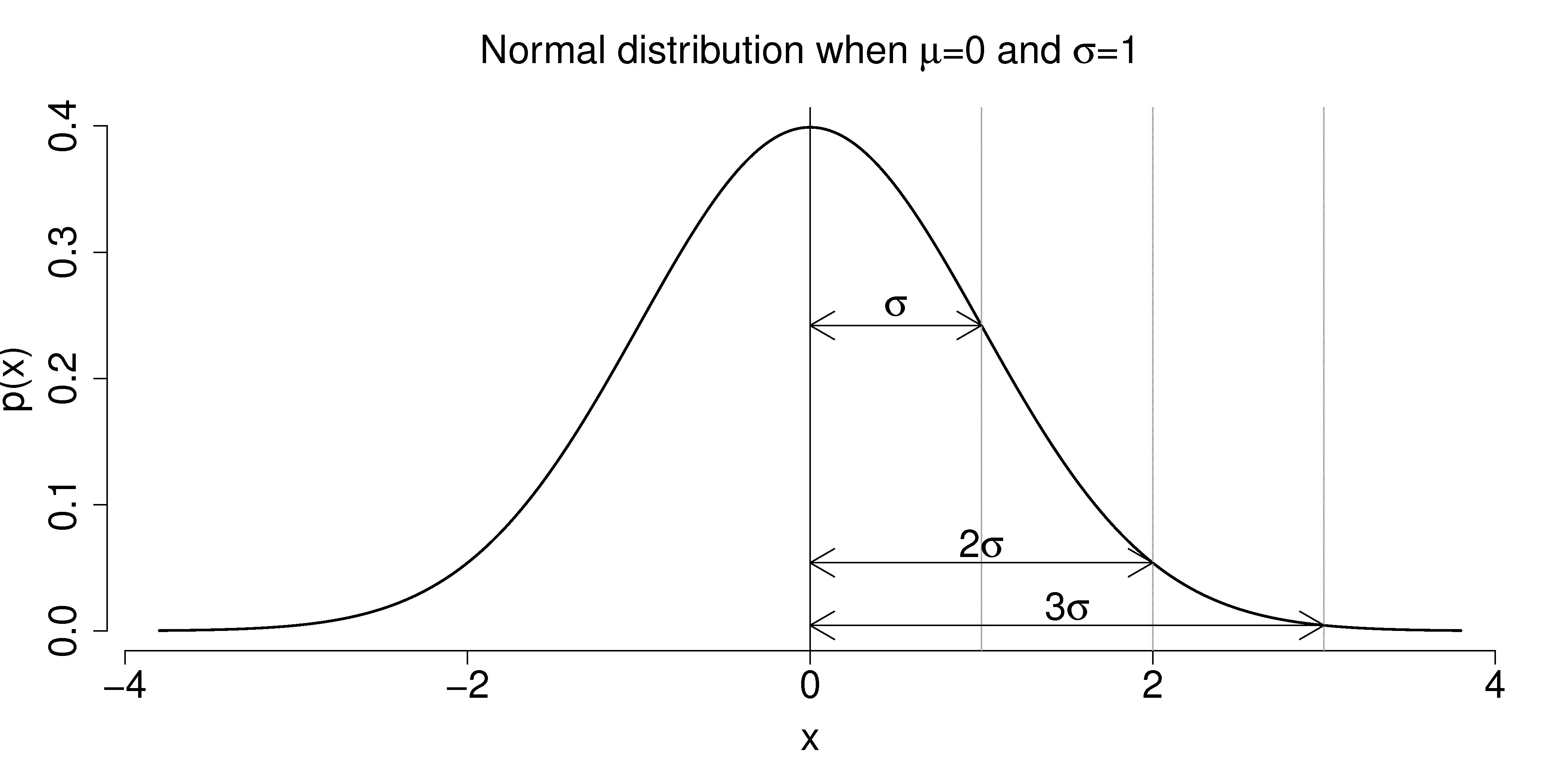
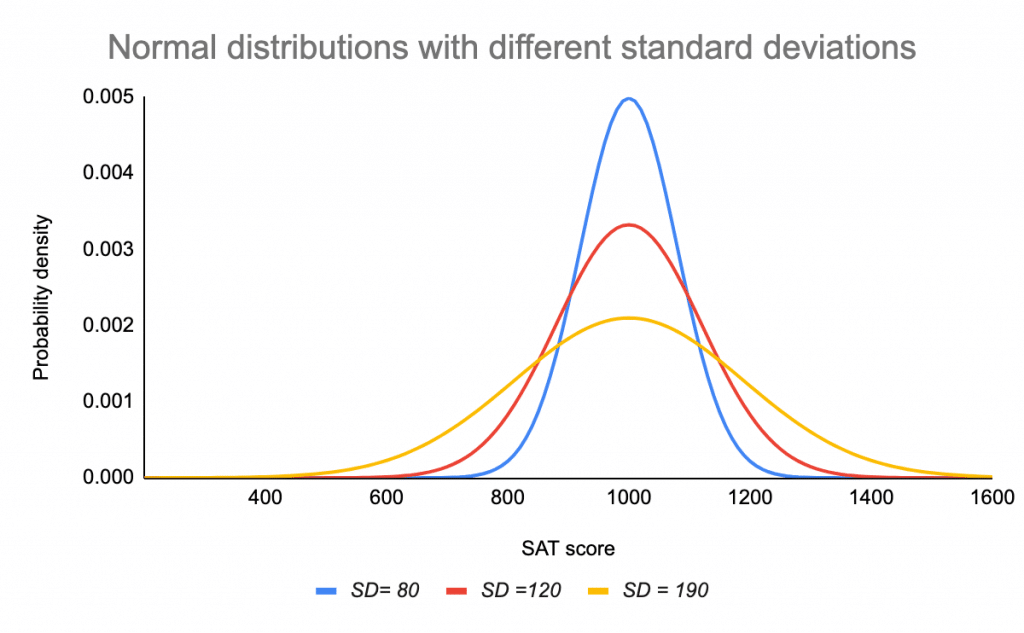
On the other hand, there are many statistical tests to check if the. The area under the curve of the normal distribution represents probabilities for the data. A graphical representation of a normal distribution is sometimes called a bell curve because of its flared shape.
Σ (“sigma”) is a population standard deviation; The precise shape can vary according to the distribution of the population but the. Here is a graph of a normal distribution with.
The general formula for the normal distribution is. The d’agostino’s k 2 test calculates summary statistics from the data, namely kurtosis and skewness, to determine if the data distribution departs from the normal.